Università degli Studi di Bari
|
|
|
- Assunta Gagliardi
- 5 anni fa
- Visualizzazioni
Transcript
1 Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1
2 CONTENTS GRAMMAR & WRITTEN EXERCISES The Present Simple Tense 3 The Present Continuous Tense 6 The Past Simple Tense 8 The Present Perfect Simple Tense 10 Comparatives & Superlatives 12 The Future 13 The Present Perfect Continuous Tense 14 COMMUNICATIVE ACTIVITIES Questions and Answers 15 All About You 16 What Time Is It? 17 My Weekends 18 Talking About The Past 19 Yes, I Have 20 Two Brothers / Quiz 21 Steven s Plans 22 Intentions / Predictions 23 Going To 24 How Long? 25 APPENDIX Pronouns / Adverbs of Frequency 26 Irregular Verbs 27 Modal Verbs / Siti Utili 29 2
3 THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare) italiano POSITIVA CONTRATTA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA io sono I am I m I m not Am I? tu sei You are You re You re not / You aren t Are you? lui è He is He s He s not / He isn t Is he? lei è She is She s She s not / She isn t Is she? esso/a è It is It s It s not / It isn t Is it? noi siamo We are We re We re not / We aren t Are we? voi siete You are You re You re not / You aren t Are you? loro sono They are They re They re not / They aren t Are they? TUTTI GLI ALTRI VERBI * per esempio, TO WORK (lavorare) italiano POSITIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA io lavoro I work I don t work Do I work? tu lavori You work You don t work Do you work? lui lavoro He works He doesn t work Does he work? lei lavora She works She doesn t work Does she work? esso/a lavora It works It doesn t work Does it work? noi lavoriamo We work We don t work Do we work? voi lavorate You work You don t work Do you work? loro lavorano They work They don t work Do they work? LA FORMA INTERROGATIVA A + S + V =? (ausiliario + soggetto + verbo = domanda) 3 PERSONA He works. He doesn t work. Does he work? 3 * vedi: Modal Verbs pagina 24
4 1. La risposta breve usa l ausiliario DO (o DOES) per ogni verbo (tranne il verbo TO BE): Do you like pop music? Ø Yes, I do. Ø No, I don t. Does your girlfriend live in Bari? Ø Yes, she does. Ø No, she doesn t. 2. Nelle forme negative e interrogative il verbo TO HAVE (avere) può essere formato, come qualsiasi verbo, con il verbo ausiliario DO/DOES (preferito negli Stati Uniti) o con GOT (più comune in Gran Bretagna): USA: Do you have a car? Does he have a sister? I don t have a pen. She doesn t have a book. GB: Have you got a car? Has he got a sister? I haven t got a pen. She hasn t got a book. 3. Se una domanda inizia con una preposizione in italiano finisce con la preposizione in inglese: Ø Di dove sei? Ø Con chi vive? Ø A cosa riferisce? Ø Fino a che ora lavorano? = Where are you from? = Who does he live with? = What does it refer to? = What time do they work until? 4. Quando il soggetto non è conosciuto non si usa il verbo ausiliario nella forma interrogativa: Ø Chi abita qua? = Who lives here? Ø Che succede dopo? = What happens after? Ø Quanti studenti sanno la risposta? = How many students know the answer? 5. La forma positiva della terza persona si forma cosi: verbo à + s She plays tennis. Eccezione: do / go à + es He does nothing. / She goes to church. s à + es She passes all the tests. ch à + es She watches TV. sh à + es It washes floors. consonante + y à + ies He studies a lot. have à has He has a car. 4
5 TRADUZIONE perché?.. chi?.. quando?.. di chi?.. dove?.. quale?.. cosa?.. come?.. 1. Di dove sei? Dove vivi? Con chi vivi? Con chi vive il tuo amico? Come si chiama lui? È difficile Non avete molto tempo Quanti anni hanno? * Perché Stefania è arrabbiata? Mi piacciono i film Rita va al lavoro in macchina A che ora ti alzi? Lui non fuma Sono le nove meno dieci Che cosa fa tuo padre?... *Numero 8: Si usa il verbo TO BE in inglese. 5
6 THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE Per parlare di azioni o situazioni in corso in questo momento, o questo periodo. TO BE +...ING TO STUDY (studiare) italiano io sto studiando tu stai studiando lui sta studiando lei sta studiando esso/a sta studiando noi stiamo studiando loro stanno studiando io non sto studiando io sto studiando? POSITIVA I am You are He is She is studying It is We are They are NEGATIVA I m not You re not / You aren t He s not / He isn t She s not / She isn t studying It s not / It isn t We re aren t / We re not They re not / They aren t INTERROGATIVA Am I Are you Is he Is she studying? Is it Are we Are they 6
7 ESERCIZIO A What are they doing? 1. She on the phone. 2. She dinner. 3. She football. 4. He ESERCIZIO B Present Simple or Present Continuous? 1. Look at that dog. It plays / is playing with a cat! 2. My mother always drives / is driving to work. 3. I can hear a baby. It cries / is crying. 4. I hate my neighbour. He listens / is listening to loud music all night, every night. 5. He s not in his office today. He works / is working at home. TRADUZIONE 1. Cosa stai facendo? Sta piovendo Suo marito non lavora oggi perché sta male Sto leggendo un libro molto interessante Dove vai?... Vado a casa. Sono stanco fare 2. piovere 3. marito male 4. leggere 5. stanco 7 = to do = to rain = husband = ill = to read = tired
8 THE PAST SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di azioni o situazioni successe in un periodo finito. TO BE (essere/stare) POSITIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA I was I wasn t Was I? You were You weren t Were you? He was He wasn t Was he? She was She wasn t Was she? It was It wasn t Was it? We were We weren t Were we? They were They weren t Were they? TUTTI GLI ALTRI VERBI...ed/didn t/did? Positiva: Negativa: Interrogativa: Yesterday I cooked lasagne. He didn t have much time. Did they study yesterday? Solo i verbi regolari. Tutti i verbi. LA PRONUNCIA VERBI REGOLARI Solo quando il verbo finisce con T o D si pronuncia l ultimo sillabo (-ED). d t tid loved cooked wanted 8 did needed
9 TRADUZIONE questo/a.. quello/a.. questi/e.. quelli/e.. 1. Cosa hai detto? Non ho sentito Siamo andati al cinema ieri Con chi sei andata in vacanza? Dove sei stato ieri sera? Hai visto la partita domenica? Abitavano a Bari da 2009 a Il suo ragazzo venne in taxi Quanto avete pagato? Loro sono andati via alle Mi è piaciuta la torta Siamo stati a casa di John sabato Paul uscì per telefonare a sua moglie Quanti anni avevi? Mio padre non aveva una televisione in casa quando era bambino dire = to say 2. sentire = to hear 3. andare = to go 4. in vacanza = on holiday 5. ieri sera = yesterday evening 6. vedere = to see la partita = the match 7. abitare = to live 8. venire = to come 9. pagare = to pay 10. via = away 11. la torta = the cake 12. la casa di John = John s house 13. uscire = to go out moglie = wife 15. bambino = little boy 9
10 THE PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE TENSE 1. Per parlare di azioni successe nel passato, ma in un periodo che continua. L informazione non è definitiva ma è vero solo finora. 2. In Gran Bretagna, quando siamo più interessati alle conseguenze attuali di un azione successa in passato, e non quando/dove ecc. è successa. (Negli Stati Uniti, però, il Past Simple è spesso usato invece del Present Perfect.) HAVE / HAS + Il PARTICIPIO PASSATO Positiva: I have written five s this week. io ho scritto... Negativa: He hasn t eaten anything today. lui non ha mangiato... Interrogativa: Have you seen the film Lincoln? avete visto... Nel Passato Prossimo italiano l ausiliario può essere avere o essere. Nel Present Perfect inglese l ausiliario è sempre avere (have o has). L uso del Present Perfect inglese non corrisponde sempre al Passato Prossimo italiano. Sia il Past Simple che il Present Perfect vengono usati per descrivere azioni successe nel passato. Ma il Past Simple si riferisce ad azioni successe in un periodo di tempo finito, mentre il Present Perfect si riferisci ad azioni successe in un periodo di tempo che continua. Periodo di tempo finito (Past Simple: ed/didn t/did?) Yesterday I smoked 3 cigarettes. Last week he didn t call me. Last month did you see any films? Last year they didn t write. Periodo di tempo che continua (Present Perfect: have/has +P.P.) Today I have smoked 3 cigarettes. This week he hasn t called me. This month have you seen any films? This year they haven t written. Il Present Perfect è usato con i seguenti avverbi di tempo: already (già usato in frasi affermative e interrogative), yet (ancora in frasi negative/già in frasi interrogative), just (appena). 10
11 ESERCIZIO Past Simple or Present Perfect? 1. a) I saw John yesterday. b) I have seen John yesterday. 2. a) Did you ever eat Indian food? b) Have you ever eaten Indian food? 3. a) Sara won 5,000 last month. b) Sara has won 5,000 last month. 4. a) I didn t read Harry Potter. b) I haven t read Harry Potter. 5. a) We got up at 6.30 today. b) We have got up at 6.30 today. 6. a) They weren t here a few minutes ago. b) They haven t been here a few minutes ago. 7. a) Barack Obama studied Law at university. b) Barack Obama has studied Law at university. 8. a) When did she call? b) When has she called? 9. a) How many Oscars did Tom Cruise win? b) How many Oscars has Tom Cruise won? 10. a) How many Oscars did Frank Sinatra win? b) How many Oscars has Frank Sinatra won? TRADUZIONE 1. Ho fatto tre esami quest anno Non ho letto il giornale oggi Non sono mai stato in America Quante volte hai visto questo film? Abbiamo studiato l inglese a scuola Non avete mai studiato questa regola Quando sei arrivato? Justin Bieber non ha mai fatto un concerto... a Bari. 9. Michael Jackson non ha mai fatto un concerto... a Bari. 10. Oh no, ho perso le mie chiave! fare un esame = to do an exam 2. leggere il giornale = to read the newspaper 4. vedere un film = to see a film 6. regola = rule 8. fare un concerto = to do a concert 10. perdere = to lose chiave = keys 11
12 COMPARATIVES AGGETTIVO ESEMPIO COMPARATIVO italiano 1 sillaba poor poorer (than...) più povero (di...) 2 sillabe + y happy happier (than...) più felice (di...) 2 sillabe o più boring interesting more boring (than...) more interesting (than...) più noioso (di...) più interessante (di...) Altre forme del comparativo: Less aggettivo than... Florence is less beautiful than Rome. As aggettivo as... Florence is as beautiful as Rome. Firenze è meno bella di Roma. Not as aggettivo as... Florence is not as beautiful as Rome. Firenze è bella quanto Roma. Firenze non è bella quanto Roma. SUPERLATIVES AGGETTIVO ESEMPIO SUPERLATIVO italiano 1 sillaba poor the poorest il più povero 2 sillaba + y happy the happiest il più felice 2 sillaba o più boring interesting the most boring the most interesting il più noioso il più interessante Altra forma del superlativo: The least aggettivo It s the least expensive. È il meno costoso.. Ci sono tre eccezioni a queste regole: AGGETTIVO COMPARATIVO SUPERLATIVO good better (than...) meglio (di...) the best il migliore bad worse (than...) peggio (di...) the worst il peggiore far further (than...) più lontano (di...) the furthest il più lontano 12
13 THE FUTURE 1. PRESENT CONTINUOUS - Per esprimere un programma preciso per il futuro, per realizzare il quale si è già fatto qualcosa. Positiva: Negativa: Interrogativa: I m having a party on Saturday. We aren t staying in a hotel. Are you getting married in church? 2. TO BE + GOING TO + VERB - Per esprimere l intenzione di fare qualcosa. - Per esprimere una previsione che si fa sulla base di una constatazione. Positiva: Negativa: Interrogativa: I m going to get up early. She isn t going to cook this evening. Are they going to come with us? 3. WILL - Previsioni*: I don t think he will win. * particolarmente dopo i verbi to suppose (supporre), to expect (aspettarsi), to think (pensare), to believe (credere) ecc. - Offerte: I ll help you. - Promesse: I won t tell anyone. - Suggerimenti: Shall we go to the cinema? Yes! Let s go now! - Decisioni prese nel momento in cui si parla: I ll have a beer, please. Positiva Negativa Interrogativa I ll I won t Shall I? / Will I? You ll You won t Will you? He/She/It ll He/She/It won t Will he? We ll We won t Shall we? / Will we? You ll You won t Will you? They ll They won t Will they? 13
14 THE PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE 1. Per esprimere un'azione che è iniziato nel passato e continua nel presente, nelle frasi con FOR o SINCE e nelle domande con HOW LONG (con i verbi che possono essere coniugati nei tempi progressivi*). Esempio: How long has it been raining? Da quanto tempo sta piovendo? It has been raining for two hours. Piove da due ore. 2. Per esprimere un'azione che è appena terminata, che si è prolungata per un certo tempo e la cui conseguenza è evidente in questo momento. Esempio: I have been working very hard. I'm exhausted! Ho lavorato molto. Sono esausto! (Ho appena finito di lavorare e la conseguenza è evidente: sono esausto.) HAVE / HAS + BEEN + IL GERUNDIO ( ing)* Positiva: They have been sleeping since 9 o clock. dormono dalle 9. Negativa: We haven t been waiting for long. non aspettiamo da molto. Interrogativa: How long has he been talking? da quanto tempo sta parlando? * Tutti i verbi hanno la ing form, ma non tutti i verbi possono essere utilizzati nei tempi progressivi. I verbi che indicano uno stato di fatto, una condizione in cui ci si trova e non un'azione dinamica, non vengono utilizzati nei tempi progressivi. I principali verbi che non vengono utilizzati nei tempi progressivi (state verbs) sono: To want (volere) To like (piacere) I verbi che indicano sentimenti (to love, amare - to hate, odiare ecc ) I verbi di percezione (to hear, udire - to see, vedere ecc ) I verbi che indicano attività intellettuale (to know, sapere - to understand, capire ecc ) I verbi che indicano possesso (to have, avere - to own, possedere) FOR = da un periodo di tempo. (I ve known John for 2 days/3weeks/4 months/5 years.) SINCE = da un tempo specifico nel passato (fin ora). (I ve known John since 9 o clock/tuesday/december/2010.) 14
15 Match the questions with the answers collegare le domande con le risposte TO BE (essere/stare) 1.? My name is Ben. 2.? I m 23 years old. 3.? I m from Dublin. 4.? I m a student. 5.? No, I m not. 6.? I m fine, thanks. Are you married? How are you? How old are you? What s your job? What s your name? Where are you from? OTHER VERBS (altri verbi) 7.? London. 8.? With two friends. 9.? One brother. His name is Steven. 10.? Yes, I have. Her name is Tina. 11.? Jazz. 12.? Every evening. 13.? My mother is a housewife. My father is retired. Have you got a girlfriend? Have you got any brothers or sisters? What do your parents do? Where do you live? What music do you like? Who do you live with? How often do you watch television? 15
16 1. What your name? My name is How old you? I am Where you from? I am from Where you live? I live in Where you go to university? I go to university in you got any brothers or sisters? Yes, I have. I ve got... / No, I haven t. 7. What type of music you to? I listen to What television programs you? I watch you any musical instruments? Yes, I do. I play... / No, I don t. 10. What languages you? I speak What sports you practice? I play... / I go... / None. 12. What food you? I like Where you usually on holiday? I usually go to... / I stay at home. 14. What your hobbies? My hobby is... / My hobbies are What time you in the morning? I get up at What you for breakfast? For breakfast I have How you to university? I come to university Where you lunch? I have lunch What you in the evening? In the evening I usually What time you to bed? I usually go to bed at... 16
17 TO PAST MINUTES TO PAST HOUR It s three o clock. It s a quarter past six. It s half past ten. It s a quarter to two. It s ten past seven. It s five to four. A B Every day Ben gets up at 1). He has a shower and he gets dressed. He has 2) for breakfast and then he goes to the university by 3). He arrives at the university at 4) and his first lesson starts at 5). At 1.15 he 6) with his 7) in the 8). In the afternoon he usually 9) in the 10). At 11) he goes home. After dinner he usually 12). He goes to bed at 13). 17
18 get On Friday evenings I home at about 5.30 in the afternoon and I just. I don t usually, but my girlfriend to my house and she dinner for me. She a professional chef and she to cook. After dinner we to music or we a film on TV. On Saturday mornings I at 9.00 and I my house. In the afternoon I football. Then in the evening I sometimes to the cinema with my friends. On Sunday mornings I in bed late. I don t until 11.00! Sometimes in the afternoon I my brother. He in the country and two children. I playing with my nephew and niece. 1. Use the correct form of these verbs to complete the spaces. usare la forma giusta di questi verbi per riempire gli spazi to get to watch to come to cook to be to get up (x2) to enjoy to go out to have to play to visit to listen to live to love to relax to stay to clean to go 2. Write the questions. scrivere le domande 1. Question:? Answer: At about 5.30 in the afternoon. 2. Question:? Answer: His girlfriend. 3. Question:? Answer: His friends. 4. Question:? Answer: In the country. 5. Question:? Answer: Two. A son and a daughter. 18
19 YOU 1. Where you born? I was born in When you born? I was born on Where you live as a child? I lived in Where you live now? I live in... SCHOOL 5. Where you go to school? I went to school in How you go to school? I went to school on foot / by What type of school you go to? I went to a you like school? Yes, I... / No, I What your favorite subject? My favorite subject was... YESTERDAY 10. What time you yesterday? I got up at you to university? Yes, I... / No, I Where you lunch? I had lunch Who you lunch with? I had lunch with What you for dinner? For dinner I had What you in the evening? In the evening I What time you to bed? I went to bed at... THE BEST HOLIDAY OF YOUR LIFE 17. Where you? I went to Who you with? I went with How you get there? I went by How long you stay for? I stayed for What the weather like? It was you like the food? Yes, I... / No, I it expensive? Yes, it... / No, it... 19
20 Have you ever been to America? Yes, I have. When did you go there? I went there two years ago. Use the verbs in the box to complete the conversations. usare i verbi nel box per completare le conversazione to break to buy to drink to drive to eat to like to live to meet to sing to sleep to spend to steal 1. A: Have you ever eaten sushi? 6. A: Have you ever your arm? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. A: Did you like it? A: How did you it? B: Yes, I liked it a lot. B: I it skiing. 2. A: Have you ever a famous person? 7. A: Have you ever abroad? B: Yes, I have. Kate Moss. B: Yes, I have. A: Where did you her? A: When did you abroad? B: I her in Rome. B: I in France as a child. 3. A: Have you ever more than 5,000? 8. A: Have you ever a Ferrari? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. A: What did you buy? A: Whose Ferrari did you? B: I a car. B: I my uncle s Ferrari. 4. A: Have you ever too much tequila? 9. A: Have you ever in public? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. A: Where did you too much tequila? A: Where did you? B: I too much tequila at my sister s party. B: I in a karaoke bar. 5. A: Have you ever in a hammock*? 10. A: Have you ever anything? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. A: How did you? A: What did you? B: I very well. B: I some sweets when I was a child. 20 * hammock = amaca
21 COMPARATIVES Ben Steven Ben and Steven are brothers. 1. Ben is than Steven. (+ young) 2. Ben is than Steven. (+ handsome) 3. Ben is than Steven. (+ friendly) 4. Ben is as Steven. (= intelligent) 5. Ben is as Steven. ( elegant) SUPERLATIVES 1. River (long) 2. University (old) 3. Building (tall) 4. Religion (ancient) 5. Man (rich) 6. City (populated) 7. Film (expensive) 8. Record (successful) 9. Planet (near)
22 morning - take car to mechanic afternoon - dentist evening - dinner at Jane s morning - swimming afternoon - poker game evening - dinner with Emma morning - gym afternoon - shopping evening - cinema with Mary morning - tennis with Fiona afternoon - French lesson evening - theatre with Angela morning - golf with Anna afternoon -meet new Au Pair evening - dinner with Susan PARIS with Lisa 1. Look at Steven s agenda for the week and answer these questions. guardare l agenda di Steve per questa settimana e rispondere a queste domande 1. What is he doing on Monday morning? 2. Where is he going on Tuesday evening? 3. Who is he having dinner with on Wednesday evening? 4. When is he playing poker? 5. What language is he studying on Friday? 2. Look at these answers and write the questions. guardare queste risposte e scrivere l domande 6. Question:? Answer: At Jane s. 7. Question:? Answer: Shopping. 8. Question:? Answer: Anna. 9. Question:? Answer: The new Au Pair. 10. Question:? Answer: At the weekend. 22
23 INTENTIONS This evening Catch a bus/train 2. Cook 3. Study 4. Go out 5. Watch a film 6. Go to bed early PREDICTIONS During my lifetime Petrol 2. Female President 3. The moon 4. Cash 5. Cancer 6. Nuclear war 23
24 Complete the sentences with going to + one of these verbs: completare le frasi con going to + uno di questi verbi put shave not jump play not eat not rain buy stay 24
25 Write the information about yourself: scrivere le informazioni su di te 1. The street where you live. I live in 2. Your best friend. My best friend s name is 3. Something you are wearing. I am wearing 4. An object which is important to you. My 5. A sport you practice. I play/go 6. A bar or restaurant you often go to. I often go to 7. A newspaper or magazine you regularly read. I regularly read 8. A book you are reading at the moment. I am reading 9. Something you can do. I can 10. Something you are learning to do. I am learning to 25
26 APPENDICE PRONOUNS Pronomi SOGGETTO OGGETTO AGGETIVO PRONOME POSSESSIVO POSSESSIVO I ME MY MINE YOU YOU YOUR YOURS HE HIM HIS HIS SHE HER HER HERS IT IT ITS ITS WE US OUR OURS YOU YOU YOUR YOURS THEY THEM THEIR THEIRS ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY gli avverbi di frequenza ALWAYS USUALLY / NORMALLY FREQUENTLY / REGULARLY OFTEN SOMETIMES OCCASIONALLY RARELY / SELDOM HARDLY EVER / ALMOST NEVER NEVER sempre di solito / normalmente frequentemente / regolarmente spesso a volte occasionalmente raramente quasi mai mai 26
27 IRREGULAR VERBS i verbi irregolari APPENDICE VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE BE essere/stare was / were been BEAT battere beat beaten BECOME diventare became become BEGIN incominciare/iniziare began begun BITE mordere bit bitten BLOW soffiare blew blown BREAK rompere broke broken BRING portare brought brought BUILD costruire built built BURN bruciare burnt or burned burnt or burned BUY comprare bought bought CATCH prendere caught caught CHOOSE scegliere chose chosen COME venire came come COST costare cost cost CUT tagliare cut cut DO fare did done DRAW disegnare drew drawn DREAM sognare dreamt or dreamed dreamt or dreamed DRINK bere drank drunk DRIVE guidare drove driven EAT mangiare ate eaten FALL cadere fell fallen FEEL sentire felt felt FIGHT lottare fought fought FIND trovare found found FLY volare flew flown FORGET dimenticare forgot forgotten GET ottenere got got GIVE dare gave given GO andare went gone GROW crescere grew grown HANG appendere hung hung HAVE avere had had HEAR sentire heard heard HIDE nascondere hid hidden HIT colpire hit hit HOLD tenere in mano held held HURT ferire/fare male hurt hurt KEEP tenere kept kept KNOW sapere/conoscere knew known LEARN imparare learnt or learned learnt or learned 27
28 VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE LEAVE lasciare/partire left left LEND prestare lent lent LET permettere/lasciare let let LIE stendersi/sdraiarsi lay lain LIGHT accendere/illuminare lit lit LOSE perdere lost lost MAKE fare made made MEAN significare meant meant MEET incontrare met met PAY pagare paid paid PUT mettere put put READ leggere read (pronunciato red ) read (pronunciato red ) RING telefonare/squillare rang rung RISE alzarsi/sorgere rose risen RUN correre ran run SAY dire said said SEE vedere saw seen SELL vendere sold sold SEND mandare sent sent SHINE splendere shone shone SHOOT sparare shot shot SHOW mostrare showed shown SHUT chiudere shut shut SING cantare sang sung SIT sedersi sat sat SLEEP dormire slept slept SMELL odorare smelt or smelled smelt or smelled SPEAK parlare spoke spoken SPEND spendere/passare spent spent STAND stare in piede stood stood STEAL rubare stole stolen SWIM nuotare swam swum TAKE prendere/portare took taken TEACH insegnare taught taught TEAR strappare tore torn TELL dire/raccontare told told THINK pensare thought thought THROW gettare threw thrown UNDERSTAND capire understood understood WAKE svegliarsi woke woken WEAR indossare wore worn WIN vincere won won WRITE scrivere wrote written 28
29 MODAL VERBS I verbi modali APPENDICE I verbi modali esprimono il modo in cui il soggetto si pone nei confronti dell azione che compie. I verbi modali in inglese sono: CAN, MUST, MAY, WILL, SHALL, WOULD, SHOULD, OUGHT Tutti i verbi modali si comportano da verbi ausiliari, cioè seguono il modello del verbo to be per quanto riguarda la costruzione interrogativa e negativa, l uso di forme contratte e le risposte brevi. Nella forma negativa sono seguiti da not. Nella forma interrogativa precedono il soggetto. Il verbo che segue un verbo modale va nella Forma Base (l infinito senza to) tranne ought. Alla terza persona singolare del Present Simple non prendono la s. Positiva: I can swim. He can drive. Negativa: I can t swim. He can t drive. Interrogativa: Can you swim? Can he drive? SITI UTILI englishgratis.com english-grammar-lessons.com englishpage.com bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/en/listen-and-watch spiegazioni in italiano della grammatica inglese. spiegazione della grammatica inglese con relativi esercizi. spiegazione della grammatica inglese con relativi esercizi. notizia con spiegazione dei vocaboli usati. video e podcast per studenti di inglese. guardian.co.uk independent.co.uk italianinsider.it thelocal.it giornale inglese giornale inglese giornale italiano in lingua inglese giornale italiano in lingua inglese YouTube lezioni video di lingua inglese youtube.com/user/hamiltonhouseelt youtube.com/user/languageplanettoluca youtube.com/user/realenglish1 youtube.com/bbclearningenglish youtube.com/user/britishcouncille 29 youtube.com/user/freeenglishlessons youtube.com/user/englishlessons4u youtube.com/user/duncaninchina youtube.com/user/minooanglolink youtube.com/user/jenniferesl
THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE
 THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare) italiano POSITIVA CONTRATTA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA io sono I am I m I m
THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare) italiano POSITIVA CONTRATTA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA io sono I am I m I m
Esempi: I have studied English and French (Ho studiato Inglese e Francese). Have you made the cake? (Hai fatto il dolce?)
 THE PRESENT PERFECT Il PRESENT PERFECT si usa per indicare un evento o una situazione che hanno conseguenze sul presente o per parlare di un'azione iniziata nel passato e che continua nel presente. I have
THE PRESENT PERFECT Il PRESENT PERFECT si usa per indicare un evento o una situazione che hanno conseguenze sul presente o per parlare di un'azione iniziata nel passato e che continua nel presente. I have
EURO IN FORMAZIONE ON LINE ANNO III MATERIA: INGLESE LEZIONE 1. Simple Past
 Simple Past Il simple past si usa: per indicare le azioni che si sono svolte nel passato ad un tempo definito, anche se non è menzionato, ma si suppone dal concetto di azione compiuta: I met him yesterday
Simple Past Il simple past si usa: per indicare le azioni che si sono svolte nel passato ad un tempo definito, anche se non è menzionato, ma si suppone dal concetto di azione compiuta: I met him yesterday
Università degli Studi di Bari
 Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1 THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare)
Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1 THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare)
Si usa. Lesson 14 (B1/B2) Present perfect simple / Present perfect continuous
 Confronta i diversi usi del present perfect simple e del present perfect continuous. Si usa PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE per parlare della DURATA (con for e since) di AZIONI/SITUAZIONI NON CONCLUSE, (azioni/situazioni
Confronta i diversi usi del present perfect simple e del present perfect continuous. Si usa PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE per parlare della DURATA (con for e since) di AZIONI/SITUAZIONI NON CONCLUSE, (azioni/situazioni
Università degli Studi di Bari
 Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1 THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare)
Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1 THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare)
Università degli Studi di Bari
 Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1 CONTENTS GRAMMAR & WRITTEN EXERCISES The Present Simple Tense 3 The Present Continuous Tense 6 The Past Simple Tense 8 The
Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1 CONTENTS GRAMMAR & WRITTEN EXERCISES The Present Simple Tense 3 The Present Continuous Tense 6 The Past Simple Tense 8 The
Lesson 5 (A1/A2) Present continuous FORMA. you / we / they are ( re) he / she / it is ( s) Interrogativa. are you / we / they is he / she / it
 Lesson 5 (A1/A2) FORMA Affermativa Interrogativa Negativa Interrogativo-negativa I am ( m) you / we / they are ( re) he / she / it is ( s) am I are you / we / they is he / she / it I am not ( m not) you
Lesson 5 (A1/A2) FORMA Affermativa Interrogativa Negativa Interrogativo-negativa I am ( m) you / we / they are ( re) he / she / it is ( s) am I are you / we / they is he / she / it I am not ( m not) you
Elementary - Lesson 3
 Elementary - Lesson 3 Il Simple Past del verbo to be Il Simple Past si usa per esprimere un azione che si è svolta in un periodo del passato, interamente trascorso. Corrisponde ai tempi italiani imperfetto,
Elementary - Lesson 3 Il Simple Past del verbo to be Il Simple Past si usa per esprimere un azione che si è svolta in un periodo del passato, interamente trascorso. Corrisponde ai tempi italiani imperfetto,
VERB TENSES:USE PRESENT SIMPLE PRESENT CONTINUOUS FUTURE-BE GOING TO FUTURE -WILL PAST SIMPLE PAST CONTINUOUS PRESENT PERFECT
 VERB TENSES:USE PRESENT SIMPLE PRESENT CONTINUOUS FUTURE-BE GOING TO FUTURE -WILL PAST SIMPLE PAST CONTINUOUS PRESENT PERFECT PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS PAST PERFECT PRESENT SIMPLE PER PARLARE DI DATI
VERB TENSES:USE PRESENT SIMPLE PRESENT CONTINUOUS FUTURE-BE GOING TO FUTURE -WILL PAST SIMPLE PAST CONTINUOUS PRESENT PERFECT PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS PAST PERFECT PRESENT SIMPLE PER PARLARE DI DATI
Ever e Never pag.2. Futuro:.Pag. 3. Comparativo di maggioranza...pag. 4. Comparativo di minoranza...pag. 5. Comparativo di uguaglianza...pag.
 Indice: Ever e Never pag.2 Present perfect + for / since. Pag. 2 Futuro:.Pag. 3 Comparativi degli aggettivi Comparativo di maggioranza...pag. 4 Comparativo di minoranza...pag. 5 Comparativo di uguaglianza...pag.5
Indice: Ever e Never pag.2 Present perfect + for / since. Pag. 2 Futuro:.Pag. 3 Comparativi degli aggettivi Comparativo di maggioranza...pag. 4 Comparativo di minoranza...pag. 5 Comparativo di uguaglianza...pag.5
Liceo Linguistico e Liceo Socio Psico Pedagogico Sperimentale Bambin Gesù San Severino Marche. Anno Scolastico 2008/2009
 Liceo Linguistico e Liceo Socio Psico Pedagogico Sperimentale Bambin Gesù San Severino Marche Anno Scolastico 2008/2009 DOCENTE: Cinzia Agostinelli MATERIA: Inglese Classe: 2ª PROGRAMMA SVOLTO GRAMMATICA
Liceo Linguistico e Liceo Socio Psico Pedagogico Sperimentale Bambin Gesù San Severino Marche Anno Scolastico 2008/2009 DOCENTE: Cinzia Agostinelli MATERIA: Inglese Classe: 2ª PROGRAMMA SVOLTO GRAMMATICA
Elementary - Lesson 4
 Elementary - Lesson 4 Il Simple Past dei verbi regolari e irregolari Abbiamo studiato precedentemente il Simple Past del verbo to be. Adesso vedremo come si forma il passato con gli altri verbi. Ricorda
Elementary - Lesson 4 Il Simple Past dei verbi regolari e irregolari Abbiamo studiato precedentemente il Simple Past del verbo to be. Adesso vedremo come si forma il passato con gli altri verbi. Ricorda
PLACEMENT TEST PER I CORSI DI INGLESE E INGLESE PREPARAZIONE AL FIRST CERTIFICATE
 PLACEMENT TEST PER I CORSI DI INGLESE E INGLESE PREPARAZIONE AL FIRST CERTIFICATE Name: Istruzioni: per ogni frase, indicare la soluzione corretta con una crocetta sulla lettera scelta LE SOLUZIONI SONO
PLACEMENT TEST PER I CORSI DI INGLESE E INGLESE PREPARAZIONE AL FIRST CERTIFICATE Name: Istruzioni: per ogni frase, indicare la soluzione corretta con una crocetta sulla lettera scelta LE SOLUZIONI SONO
PASSIVE VOICE. Costruzione attiva e costruzione passiva
 PASSIVE VOICE Costruzione attiva e costruzione passiva In una frase attiva (active voice), il soggetto compie attivamente l azione espressa dal verbo: Mark reads a book. Nella frase passiva (passive voice)
PASSIVE VOICE Costruzione attiva e costruzione passiva In una frase attiva (active voice), il soggetto compie attivamente l azione espressa dal verbo: Mark reads a book. Nella frase passiva (passive voice)
Basic English Grammar. long forms short forms long forms short forms
 Lesson 29 www.englishforitalians.com 1 contractions abbreviazioni to be (present simple) I am I m I am not I ----- you are you re you are not you aren t he is he s he is not he isn t she is she s she is
Lesson 29 www.englishforitalians.com 1 contractions abbreviazioni to be (present simple) I am I m I am not I ----- you are you re you are not you aren t he is he s he is not he isn t she is she s she is
Lesson 8 (A2) Past simple: forma affermativa. Past simple verbi regolari - forma affermativa. I / we / you / they. forma base del verbo + -ed
 Lesson 8 (A2) Past simple: forma affermativa Past simple verbi regolari - forma affermativa I / we / you / they he / she / it forma base del verbo + -ed Il past simple dei verbi regolari si forma aggiungendo
Lesson 8 (A2) Past simple: forma affermativa Past simple verbi regolari - forma affermativa I / we / you / they he / she / it forma base del verbo + -ed Il past simple dei verbi regolari si forma aggiungendo
Practice phrases for class 12
 Practice phrases for class 12 Write in the blank yes if you can use the trapassato prossimo in that sentence and no if you cannot. I have done the first one for you. Carlo was happy because had finished
Practice phrases for class 12 Write in the blank yes if you can use the trapassato prossimo in that sentence and no if you cannot. I have done the first one for you. Carlo was happy because had finished
Sia must che have to esprimono necessità e obbligo. 1. Must esprime un obbligo imposto da chi parla, o sentito personalmente come un dovere.
 Lesson 32 www.englishforitalians.com 1 must - have to must Sia must che have to esprimono necessità e obbligo. 1. Must esprime un obbligo imposto da chi parla, o sentito personalmente come un dovere. >
Lesson 32 www.englishforitalians.com 1 must - have to must Sia must che have to esprimono necessità e obbligo. 1. Must esprime un obbligo imposto da chi parla, o sentito personalmente come un dovere. >
Il Present Continuous per il futuro e to have to
 Beginner - Lesson 10 Il Present Continuous per il futuro e to have to Come abbiamo visto nella lezione precedente, il Present Continuous è usato per esprimere azioni che avvengono nel momento in cui si
Beginner - Lesson 10 Il Present Continuous per il futuro e to have to Come abbiamo visto nella lezione precedente, il Present Continuous è usato per esprimere azioni che avvengono nel momento in cui si
affermativa sogg. + have ( ve) / has ( s) + participio passato interrogativa have/has + sogg. + participio passato?
 Il present perfect simple si costruisce con: have/has + participio passato del verbo Forma affermativa sogg. + have ( ve) / has ( s) + participio passato interrogativa have/has + sogg. + participio passato?
Il present perfect simple si costruisce con: have/has + participio passato del verbo Forma affermativa sogg. + have ( ve) / has ( s) + participio passato interrogativa have/has + sogg. + participio passato?
Lesson 18 (B2) Future continuous. Forma
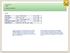 Forma affermativa sogg. + will ( ll) + be + forma in -ing interrogativa will + sogg. + be + forma in -ing? negativa sogg. + will not (won t) + be + forma in -ing interrogativo-negativa won t + sogg. +
Forma affermativa sogg. + will ( ll) + be + forma in -ing interrogativa will + sogg. + be + forma in -ing? negativa sogg. + will not (won t) + be + forma in -ing interrogativo-negativa won t + sogg. +
PRESENT SIMPLE VERB TO BE (essere)
 PRESENT SIMPLE VERB TO BE (essere) AFFIRMATIVE FULL FORMS SHORT FORMS I AM Io sono I'M Io sono YOU ARE Tu sei YOU'RE Tu sei HE IS Egli è HE'S Egli è SHE IS Ella è SHE'S Ella è IT IS Esso/a è IT'S Esso/a
PRESENT SIMPLE VERB TO BE (essere) AFFIRMATIVE FULL FORMS SHORT FORMS I AM Io sono I'M Io sono YOU ARE Tu sei YOU'RE Tu sei HE IS Egli è HE'S Egli è SHE IS Ella è SHE'S Ella è IT IS Esso/a è IT'S Esso/a
TO BE - SIMPLE PRESENT
 TO BE - SIMPLE PRESENT A differenza degli altri verbi inglesi il cui uso del Simple Present non coincide sempre con ilpresente Indicativo italiano, il Simple Present del verbo To be traduce generalmente
TO BE - SIMPLE PRESENT A differenza degli altri verbi inglesi il cui uso del Simple Present non coincide sempre con ilpresente Indicativo italiano, il Simple Present del verbo To be traduce generalmente
Base form Simple Past Past Participle Work Worked Worked Lavorai/lavoravo/ho lavorato. Il paradigma di un verbo irregolare è da sapere a memoria.
 1 PASSATI A CONFRONTO: Prima di ripassare i passati, ripassiamo cos è un paradigma. Paradigma viene dal greco, significa esempio o modello. È un modello da ricordare a memoria perché torna utile quando
1 PASSATI A CONFRONTO: Prima di ripassare i passati, ripassiamo cos è un paradigma. Paradigma viene dal greco, significa esempio o modello. È un modello da ricordare a memoria perché torna utile quando
Il Present Simple nella forma interrogativa. Ausiliare do/does + soggetto + verbo principale (all infinito senza to ) + ulteriori determinazioni +?
 Beginner - Lesson 6 Il Present Simple nella forma interrogativa Domande che richiedono risposte brevi La forma interrogativa del Present Simple (presente indicativo) si costruisce con l ausiliare do (
Beginner - Lesson 6 Il Present Simple nella forma interrogativa Domande che richiedono risposte brevi La forma interrogativa del Present Simple (presente indicativo) si costruisce con l ausiliare do (
Integrazione allo studio di. Inglese B1. a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori
 Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Grammatica inglese Milia INGLESE. davanti a parole che iniziano per consonante e con suono iu : a dog, a european car
 INGLESE ARTICOLO DETERMINATIVO (il, lo, la, i, gli, le) The INDETERMINATIVO (un, uno, una) A An davanti a parole che iniziano per consonante e con suono iu : a dog, a european car davanti a parole che
INGLESE ARTICOLO DETERMINATIVO (il, lo, la, i, gli, le) The INDETERMINATIVO (un, uno, una) A An davanti a parole che iniziano per consonante e con suono iu : a dog, a european car davanti a parole che
Future perfect simple
 Lesson 19 (B2) Future perfect simple e future perfect continuous Future perfect simple Forma affermativa sogg. + will ( ll) have + participio passato interrogativa will + sogg. + have + participio passato?
Lesson 19 (B2) Future perfect simple e future perfect continuous Future perfect simple Forma affermativa sogg. + will ( ll) have + participio passato interrogativa will + sogg. + have + participio passato?
Integrazione allo studio di. Inglese B1. a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori
 Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Forma Costruzione Esempio forma affermativa SOGGETTO + FORMA BASE (+ s alla 3 persona sing.) DO NOT = DON'T DOES NOT = DOESN'T
 forma affermativa SOGGETTO + FORMA BASE (+ s alla 3 persona sing.) I work you work he/she/it works we work you work forma negativa SOGGETTO + DO / DOES + NOT + FORMA BASE they work I do not work (I don
forma affermativa SOGGETTO + FORMA BASE (+ s alla 3 persona sing.) I work you work he/she/it works we work you work forma negativa SOGGETTO + DO / DOES + NOT + FORMA BASE they work I do not work (I don
Integrazione allo studio di. Inglese B1. a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori
 Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
SIMPLE PAST VERB TO BE (essere)
 SIMPLE PAST VERB TO BE (essere) Il simple past si usa per indicare situazioni e fatti che sono cominciati e terminati nel passato, anche se sono conclusi da poco tempo. This morning I was at school = questa
SIMPLE PAST VERB TO BE (essere) Il simple past si usa per indicare situazioni e fatti che sono cominciati e terminati nel passato, anche se sono conclusi da poco tempo. This morning I was at school = questa
Lesson 24: Prepositions of Time. (in, on, at, for, during, before, after) Lezione 24: Preposizioni di tempo. Come usare le preposizioni di tempo.
 Lesson 24: Prepositions of Time (in, on, at, for, during, before, after) Lezione 24: Preposizioni di tempo Come usare le preposizioni di tempo. Reading (Lettura) I was born in 2000. (Sono nato nel 2000)
Lesson 24: Prepositions of Time (in, on, at, for, during, before, after) Lezione 24: Preposizioni di tempo Come usare le preposizioni di tempo. Reading (Lettura) I was born in 2000. (Sono nato nel 2000)
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Venticinque
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Venticinque U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio M Today we do another exercise U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Venticinque U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio M Today we do another exercise U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare
Classroom language QUESTIONS
 Classroom language QUESTIONS Chiedi alla tua insegnante se puoi chiedere qualcosa Excuse me, can I ask something? Chiedi se puoi dire qualcosa? Can I say something? Chiedi il significato di apologise What
Classroom language QUESTIONS Chiedi alla tua insegnante se puoi chiedere qualcosa Excuse me, can I ask something? Chiedi se puoi dire qualcosa? Can I say something? Chiedi il significato di apologise What
VERBI MODALI. MUST o HAVE TO. SCEGLI L'ALTERNATIVA CORRETTA.
 VERBI MODALI CAN, COULD, MAY. SCEGLI L'ALTERNATIVA CORRETTA. 1. I COULD/ CAN dance very well. COULD / CAN you? 2. Richard CAN/COULD talk when he was ten months. 3. I CAN/COULD see Tim. He is over there.
VERBI MODALI CAN, COULD, MAY. SCEGLI L'ALTERNATIVA CORRETTA. 1. I COULD/ CAN dance very well. COULD / CAN you? 2. Richard CAN/COULD talk when he was ten months. 3. I CAN/COULD see Tim. He is over there.
simple past to be = essere verbi regolari / irregular I was / wasn't you were / weren't he she it was we were you were they were
 simple past to be = essere verbi regolari / irregolari I was / wasn't you were / weren't he she it was we were you were they were Was I? Were you..? regular irregular affirmative -ED/ -IED vedi tabella
simple past to be = essere verbi regolari / irregolari I was / wasn't you were / weren't he she it was we were you were they were Was I? Were you..? regular irregular affirmative -ED/ -IED vedi tabella
Il verbo To be è talvolta utilizzato in Inglese in espressioni in cui in Italiano si usano altri verbi.
 Quali tra le seguenti frasi italiane, presenta il verbo essere? 1. Io vado al mercato 2. Loro cantano le canzoni di natale. 3. Lei è alta. 4. Lui porta gli occhiali. 5. Noi siamo in anticipo. 6. Hai la
Quali tra le seguenti frasi italiane, presenta il verbo essere? 1. Io vado al mercato 2. Loro cantano le canzoni di natale. 3. Lei è alta. 4. Lui porta gli occhiali. 5. Noi siamo in anticipo. 6. Hai la
Lower intermediate - Lesson 5
 Lower intermediate - Lesson 5 Le domande con il Simple Past Nelle lezioni precedenti abbiamo studiato il Simple Past dei verbi regolari e irregolari. Abbiamo visto come si forma il passato di questi verbi
Lower intermediate - Lesson 5 Le domande con il Simple Past Nelle lezioni precedenti abbiamo studiato il Simple Past dei verbi regolari e irregolari. Abbiamo visto come si forma il passato di questi verbi
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventuno
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventuno U Oggi, facciamo un esercizio M Today we do an exercise U Oggi, facciamo un esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare a come dirla in italiano:
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventuno U Oggi, facciamo un esercizio M Today we do an exercise U Oggi, facciamo un esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare a come dirla in italiano:
PRESENT TENSE. = things that happen according to a schedule
 FUTURE PRESENT TENSE = things that happen according to a schedule Examples: What time does the film start? It starts at 8 o clock. What time does the train leave? It leaves at 9 am. When is the library
FUTURE PRESENT TENSE = things that happen according to a schedule Examples: What time does the film start? It starts at 8 o clock. What time does the train leave? It leaves at 9 am. When is the library
Tessere per giocare al gioco dell'oca oppure per domanda e rispost a a punti
 Tessere per giocare al gioco dell'oca oppure per domanda e rispost a a punti Ci sono: Domande in inglese e relativa risposta Istruzioni Prima di tirare il dado è necessario pescare una di queste tessere
Tessere per giocare al gioco dell'oca oppure per domanda e rispost a a punti Ci sono: Domande in inglese e relativa risposta Istruzioni Prima di tirare il dado è necessario pescare una di queste tessere
PRESENT SIMPLE. Indicativo Presente = Presente Abituale. Tom s everyday life
 PRESENT SIMPLE Indicativo Presente = Presente Abituale Prerequisiti: - Pronomi personali soggetto e complemento - Aggettivi possessivi - Esprimere l ora - Presente indicativo dei verbi essere ed avere
PRESENT SIMPLE Indicativo Presente = Presente Abituale Prerequisiti: - Pronomi personali soggetto e complemento - Aggettivi possessivi - Esprimere l ora - Presente indicativo dei verbi essere ed avere
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Quindici
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Quindici U Buongiorno, anche in questa lezione iniziamo con qualche dialogo formale M Good morning, in this lesson as well, let s start with some formal dialogues U Buongiorno,
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Quindici U Buongiorno, anche in questa lezione iniziamo con qualche dialogo formale M Good morning, in this lesson as well, let s start with some formal dialogues U Buongiorno,
Lesson 42: have to, don t have to. Lezione 42: devo, non devo
 Lesson 42: have to, don t have to Lezione 42: devo, non devo Reading (Lettura) We have to go to school tomorrow. ( Dobbiamo andare a scuola domani ) I have to get up at 5 am tomorrow. ( Devo alzarmi alle
Lesson 42: have to, don t have to Lezione 42: devo, non devo Reading (Lettura) We have to go to school tomorrow. ( Dobbiamo andare a scuola domani ) I have to get up at 5 am tomorrow. ( Devo alzarmi alle
Forma affermativa Forma negativa Forma interrogativa. I was not. you were not. he-she-it was not. we were not. you were not.
 SIMPLE PAST A differenza di tutti gli altri verbi inglesi che, al Simple Past, utilizzano la stessa forma per tutte le persone, il verbo to be ha due forme per il Simple Past: WAS e WERE. Forma affermativa
SIMPLE PAST A differenza di tutti gli altri verbi inglesi che, al Simple Past, utilizzano la stessa forma per tutte le persone, il verbo to be ha due forme per il Simple Past: WAS e WERE. Forma affermativa
IL PRESENT PERFECT. l ausiliare TO HAVE coniugato have o has a seconda del soggetto. il PARTICIPIO PASSATO del verbo interessato
 IL PRESENT PERFECT Il Present Perfect è formato da tre elementi: il soggetto l ausiliare TO HAVE coniugato have o has a seconda del soggetto il PARTICIPIO PASSATO del verbo interessato Riguardo al participio
IL PRESENT PERFECT Il Present Perfect è formato da tre elementi: il soggetto l ausiliare TO HAVE coniugato have o has a seconda del soggetto il PARTICIPIO PASSATO del verbo interessato Riguardo al participio
infinitive past simple past participle to be = essere, stare was/were = ero, stavo been = stato fui, stetti
 Lesson 36 www.englishforitalians.com 1 1. Past Simple to be infinitive past simple past participle to be = essere, stare was/were = ero, stavo been = stato fui, stetti I was was I? you were were you? he
Lesson 36 www.englishforitalians.com 1 1. Past Simple to be infinitive past simple past participle to be = essere, stare was/were = ero, stavo been = stato fui, stetti I was was I? you were were you? he
BASIC TENSES by Lewis Baker PRESENT SIMPLE (ausiliare do al neg ed interrog; verbo all infinito)
 BASIC TENSES 8. PRESENT SIMPLE (ausiliare do al neg ed interrog; verbo all infinito) I work I don t work Do I work? You work You don t work Do you work? He, she, it works He, she, it doesn t work Does
BASIC TENSES 8. PRESENT SIMPLE (ausiliare do al neg ed interrog; verbo all infinito) I work I don t work Do I work? You work You don t work Do you work? He, she, it works He, she, it doesn t work Does
Integrazione allo studio di. Inglese B1. a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori
 Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventisei
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventisei M What are you doing? U Cosa stai facendo? M What are you doing? F I am eating. D Sto mangiando F I am eating. M And you? What are you doing? U E tu? Cosa stai facendo?
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventisei M What are you doing? U Cosa stai facendo? M What are you doing? F I am eating. D Sto mangiando F I am eating. M And you? What are you doing? U E tu? Cosa stai facendo?
SUMMER HOMEWORK! Name: Surname: Class: School year: Indice:
 SUMMER HOMEWORK! Name: Surname: Class: School year: Indice: 1. GRAMMAR. Durante l estate dovrai trascrivere solo le parti blu del tuo libro di testo su un quaderno piccolo: pagine 10 e 11; pagine 18 e
SUMMER HOMEWORK! Name: Surname: Class: School year: Indice: 1. GRAMMAR. Durante l estate dovrai trascrivere solo le parti blu del tuo libro di testo su un quaderno piccolo: pagine 10 e 11; pagine 18 e
Il verbo modale can (potere, sapere) presenta le seguenti caratteristiche: a) è sempre seguito dal verbo principale all infinito senza to ;
 Beginner - Lesson 7 Il verbo modale can Il verbo modale can (potere, sapere) presenta le seguenti caratteristiche: a) è sempre seguito dal verbo principale all infinito senza to ; b) non prende la desinenza
Beginner - Lesson 7 Il verbo modale can Il verbo modale can (potere, sapere) presenta le seguenti caratteristiche: a) è sempre seguito dal verbo principale all infinito senza to ; b) non prende la desinenza
Materia: INGLESE Data: 24/10/2004
 ! VERBI CHE TERMINANO IN... COME COSTRUIRE IL SIMPLE PAST ESEMPIO e aggiungere -d live - lived date - dated consonante + y 1 vocale + 1 consonante (ma non w o y) cambiare y in i, poi aggiungere -ed raddoppiare
! VERBI CHE TERMINANO IN... COME COSTRUIRE IL SIMPLE PAST ESEMPIO e aggiungere -d live - lived date - dated consonante + y 1 vocale + 1 consonante (ma non w o y) cambiare y in i, poi aggiungere -ed raddoppiare
Periodo ipotetico di III tipo
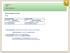 Lesson 22 (B2) Third contitional Periodo ipotetico di III tipo Forma Frase subordinata If + sogg. + past perfect (had + participio passato) If she had invited me, Se mi avesse invitato, Frase principale
Lesson 22 (B2) Third contitional Periodo ipotetico di III tipo Forma Frase subordinata If + sogg. + past perfect (had + participio passato) If she had invited me, Se mi avesse invitato, Frase principale
Passive form. The wolf eats the lamb. The lamb is eaten by the wolf. Subj. + TO BE + Past Participle.
 Passive form The wolf eats the lamb. The lamb is eaten by the wolf. Subj. + TO BE + Past Participle. The lamb is eaten. Is the lamb eaten? The lamb isn't eaten. 1. Si usa la forma passiva quando non si
Passive form The wolf eats the lamb. The lamb is eaten by the wolf. Subj. + TO BE + Past Participle. The lamb is eaten. Is the lamb eaten? The lamb isn't eaten. 1. Si usa la forma passiva quando non si
To get Il verbo get. Expressions with get Espressioni con get
 1 To get Il verbo get Il verbo to get è uno dei più utili, comuni e utilizzati nella lingua inglese. Ecco una serie di espressioni costruite con get. Osserva come cambia di significato: Get a taxi to the
1 To get Il verbo get Il verbo to get è uno dei più utili, comuni e utilizzati nella lingua inglese. Ecco una serie di espressioni costruite con get. Osserva come cambia di significato: Get a taxi to the
Comparatives and Superlative Comparativi e superlativi
 1 Comparatives and Superlative Comparativi e superlativi Iniziamo col rivedere la forma comparativa dell'aggettivo. Ricordiamo che il comparativo si usa per paragonare due cose o due persone. Il comparativo
1 Comparatives and Superlative Comparativi e superlativi Iniziamo col rivedere la forma comparativa dell'aggettivo. Ricordiamo che il comparativo si usa per paragonare due cose o due persone. Il comparativo
IL DISCORSO INDIRETTO
 IL DISCORSO INDIRETTO Il discorso indiretto (o riportato ) si usa per riportare parole, discorsi e opinioni di altre persone. Per trasformare il discorso diretto in discorso indiretto serve innanzitutto
IL DISCORSO INDIRETTO Il discorso indiretto (o riportato ) si usa per riportare parole, discorsi e opinioni di altre persone. Per trasformare il discorso diretto in discorso indiretto serve innanzitutto
Lesson 41: may, might, might not. Lezione 41: puoi, potresti, non potresti
 Lesson 41: may, might, might not Lezione 41: puoi, potresti, non potresti Reading (Lettura) You may have a seat. ( Puoi sederti ) May I borrow your book? ( Posso prendere in prestito il tuo libro?) The
Lesson 41: may, might, might not Lezione 41: puoi, potresti, non potresti Reading (Lettura) You may have a seat. ( Puoi sederti ) May I borrow your book? ( Posso prendere in prestito il tuo libro?) The
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Tredici
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Tredici U Francesca, tu capisci l inglese? M Francesca, do you understand English? U Francesca, tu capisci l inglese? D Non lo capisco molto bene. Perché? M I don t understand
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Tredici U Francesca, tu capisci l inglese? M Francesca, do you understand English? U Francesca, tu capisci l inglese? D Non lo capisco molto bene. Perché? M I don t understand
CORSO BASE DI INGLESE
 CORSO BASE DI INGLESE Lezione 10 Docente: Dott.ssa Sara Livio WWW.LEZIONE-ONLINE.IT Passato semplice: verbo essere Passato semplice verbo essere (past simple of to be) Passato semplice: verbo essere Il
CORSO BASE DI INGLESE Lezione 10 Docente: Dott.ssa Sara Livio WWW.LEZIONE-ONLINE.IT Passato semplice: verbo essere Passato semplice verbo essere (past simple of to be) Passato semplice: verbo essere Il
Riallineamento-Test Finale di Autovalutazione LINGUA INGLESE
 SURNAME AND NAME STUDENT NUMBER DATE COPIA DESTINATA AL RIALLINEAMENTO AUTONOMO-INDIVIDUALE DEGLI STUDENTI UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI CAGLIARI Facoltà di Scienze Economiche, Giuridiche e Politiche Riallineamento-Test
SURNAME AND NAME STUDENT NUMBER DATE COPIA DESTINATA AL RIALLINEAMENTO AUTONOMO-INDIVIDUALE DEGLI STUDENTI UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI CAGLIARI Facoltà di Scienze Economiche, Giuridiche e Politiche Riallineamento-Test
PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE 2017/2018 LINGUA E CIVILTA INGLESE AB24. CLASSI SECONDE TECNICO DOCENTI: Buffagni Anna
 ISTITUTO DI ISTRUZIONE SUPERIORE ANGELO MOTTI PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE 2017/2018 LINGUA E CIVILTA INGLESE AB24 CLASSI SECONDE TECNICO DOCENTI: Buffagni Anna Legenda: in corsivo si indicano gli obiettivi
ISTITUTO DI ISTRUZIONE SUPERIORE ANGELO MOTTI PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE 2017/2018 LINGUA E CIVILTA INGLESE AB24 CLASSI SECONDE TECNICO DOCENTI: Buffagni Anna Legenda: in corsivo si indicano gli obiettivi
100 QUIZ IN LINGUA INGLESE
 1 ANTEPRIMA Stai leggendo un estratto gratuito VERSIONE DEMO GRATUITA 100 QUIZ IN LINGUA INGLESE Francesca Desiderio Edizioni: concorsipubblici.com Acquista online ebook completo 2 100 Quiz in lingua inglese
1 ANTEPRIMA Stai leggendo un estratto gratuito VERSIONE DEMO GRATUITA 100 QUIZ IN LINGUA INGLESE Francesca Desiderio Edizioni: concorsipubblici.com Acquista online ebook completo 2 100 Quiz in lingua inglese
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Quattordici
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Quattordici F Hi. A bit of grammar today Do you remember? In Italian, there are two ways to address people. You can either talk to someone in an informal way, for example
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Quattordici F Hi. A bit of grammar today Do you remember? In Italian, there are two ways to address people. You can either talk to someone in an informal way, for example
Copyright Esselibri S.p.A.
 1) I tomorrow at 7.30 a) am leaving b) will leave c) shall leave d) shall to leave QUESTIONARIO N. 2 LINGUA INGLESE (II LIVELLO) Inserire la forma verbale corretta. 2) I want to go to the cinema with my
1) I tomorrow at 7.30 a) am leaving b) will leave c) shall leave d) shall to leave QUESTIONARIO N. 2 LINGUA INGLESE (II LIVELLO) Inserire la forma verbale corretta. 2) I want to go to the cinema with my
Lesson 28: Other Prepositions. (by, about, like, of, with, without) Lezione 28: Altre Preposizioni. Come utilizzare le altre preposizioni.
 Lesson 28: Other Prepositions (by, about, like, of, with, without) Lezione 28: Altre Preposizioni Come utilizzare le altre preposizioni. Reading (Lettura) I go to school by bus. ( Vado a scuola in autobus
Lesson 28: Other Prepositions (by, about, like, of, with, without) Lezione 28: Altre Preposizioni Come utilizzare le altre preposizioni. Reading (Lettura) I go to school by bus. ( Vado a scuola in autobus
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventiquattro
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventiquattro U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio M Today we do another exercise U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventiquattro U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio M Today we do another exercise U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare
PROVA DI INGLESE PER STUDENTI DI MADRELINGUA NON ITALIANA
 Ministero della Pubblica Istruzione Rilevazione degli apprendimenti Anno Scolastico 2006-2007 PROVA DI INGLESE PER STUDENTI DI MADRELINGUA NON ITALIANA Scuola Secondaria di II grado Classe Prima inglese_prima
Ministero della Pubblica Istruzione Rilevazione degli apprendimenti Anno Scolastico 2006-2007 PROVA DI INGLESE PER STUDENTI DI MADRELINGUA NON ITALIANA Scuola Secondaria di II grado Classe Prima inglese_prima
Verbi regolari. Esempi: ( nella traduzione ci sono 2 verbi) Look I looked ( ho guardato) We wanted ( abbiamo voluto) They played ( hanno giocato)
 TEMPI: Past simple Il past simple si forma aggiungendo ED Alla forma base del verbo, Ma ci sono dei verbi irregolari( Pag.127) che hanno una forma tutta personale. Verbi regolari Esempi: ( nella traduzione
TEMPI: Past simple Il past simple si forma aggiungendo ED Alla forma base del verbo, Ma ci sono dei verbi irregolari( Pag.127) che hanno una forma tutta personale. Verbi regolari Esempi: ( nella traduzione
I don't work Io non lavoro. He doesn't work Egli non lavora. He didn't work Egli non lavorava. He didn't eat Egli non mangiava
 Forma affermativa Forma negativa Forma Interrogativa Simple present Azioni che avvengono regolarmente Opinioni Condizioni Sogg.+ verbo all'infinito I work Io lavoro He works Egli lavora Sogg + do + not
Forma affermativa Forma negativa Forma Interrogativa Simple present Azioni che avvengono regolarmente Opinioni Condizioni Sogg.+ verbo all'infinito I work Io lavoro He works Egli lavora Sogg + do + not
schema soggetto Verbo be Past participle By + chi compie l azione Writers are hired By the producers
 Forma passiva Ripassiamo la frase passiva in italiano: Il soggetto subisce l azione Il verbo è composto da essere+ part.passato A volte il verbo essere viene sostituito da venire ma sempre deve essere
Forma passiva Ripassiamo la frase passiva in italiano: Il soggetto subisce l azione Il verbo è composto da essere+ part.passato A volte il verbo essere viene sostituito da venire ma sempre deve essere
Per poter mettere un verbo al Simple Past devono verificarsi contemporaneamente tre condizioni.
 Quando si usa Il Simple Past è il tempo verbale inglese che esprime il concetto generale di un azione che si è svolta nel passato e non ha più nessun rapporto con il presente. Per poter mettere un verbo
Quando si usa Il Simple Past è il tempo verbale inglese che esprime il concetto generale di un azione che si è svolta nel passato e non ha più nessun rapporto con il presente. Per poter mettere un verbo
Lesson 17: Can, Cannot, Can...?
 Lesson 17: Can, Cannot, Can...? Lezione 17 : Puoi, Non puoi? Reading (Leggere) I can walk. (Io posso camminare) He can write an email. (Lui può scrivere una mail) You can dance. (Tu puoi ballare) They
Lesson 17: Can, Cannot, Can...? Lezione 17 : Puoi, Non puoi? Reading (Leggere) I can walk. (Io posso camminare) He can write an email. (Lui può scrivere una mail) You can dance. (Tu puoi ballare) They
BOOKLET ENGLISH PRIMARIA- CLASSE QUINTA
 Prove di conoscenza delle lingue francese e inglese di cui all'art. 6 delle legge regionale n. 18/2016 (Decreto Assessore all'istruzione e Cultura n 20858/SS del 16 ottobre 2017) BOOKLET ENGLISH PRIMARIA-
Prove di conoscenza delle lingue francese e inglese di cui all'art. 6 delle legge regionale n. 18/2016 (Decreto Assessore all'istruzione e Cultura n 20858/SS del 16 ottobre 2017) BOOKLET ENGLISH PRIMARIA-
Lesson 3 (A1/A2) Present simple forma affermativa. Forma
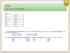 Lesson 3 (A1/A2) Present simple forma affermativa Forma I you he, she, it we you they s La forma affermativa del present simple si costruisce con l infinito senza to per tutte le persone, tranne la 3 a
Lesson 3 (A1/A2) Present simple forma affermativa Forma I you he, she, it we you they s La forma affermativa del present simple si costruisce con l infinito senza to per tutte le persone, tranne la 3 a
To be, negative contractions Essere, le contrazioni della forma negativa
 To be, interrogative Essere, forma interrogativa 1 Per fare una domanda si mette prima il verbo e poi il pronome, cioè si compie un'inversione. Nella domanda non si usa la forma contratta. To be forma
To be, interrogative Essere, forma interrogativa 1 Per fare una domanda si mette prima il verbo e poi il pronome, cioè si compie un'inversione. Nella domanda non si usa la forma contratta. To be forma
ESAME DI QUALIFICA TRIENNALE (II LIVELLO EUROPEO)
 Nome e Cognome Id Azione Data.. Tipo prova INGLESE - III anno - sessione 1 a.f. 2008/2009 ESAME DI QUALIFICA TRIENNALE (II LIVELLO EUROPEO) LEGGI ATTENTAMENTE LE SEGUENTI FRASI, CHE RAPPRESENTANO POSSIBILI
Nome e Cognome Id Azione Data.. Tipo prova INGLESE - III anno - sessione 1 a.f. 2008/2009 ESAME DI QUALIFICA TRIENNALE (II LIVELLO EUROPEO) LEGGI ATTENTAMENTE LE SEGUENTI FRASI, CHE RAPPRESENTANO POSSIBILI
INDICATIVO/PRESENTE VERBO ESSERE TO BE I am io sono you are tu sei he/she/it is egli/ella/esso è we are noi siamo you are voi siete they are essi sono
 Appunti Inglese INDICATIVO/PRESENTE VERBO ESSERE TO BE I am io sono you are tu sei he/she/it is egli/ella/esso è we are noi siamo you are voi siete they are essi sono INDICATIVO/PRESENTE VERBO AVERE TO
Appunti Inglese INDICATIVO/PRESENTE VERBO ESSERE TO BE I am io sono you are tu sei he/she/it is egli/ella/esso è we are noi siamo you are voi siete they are essi sono INDICATIVO/PRESENTE VERBO AVERE TO
Present Perfect. Forma affermativa: SOGGETTO + HAVE + PARTIPIO PASSATO
 Present Perfect Present Perfect: forme Present Perfect: funzioni Present Perfect: usi più comuni (senza l impiego di espressioni di tempo) Present Perfect: usi più comuni (con l impiego di espressioni
Present Perfect Present Perfect: forme Present Perfect: funzioni Present Perfect: usi più comuni (senza l impiego di espressioni di tempo) Present Perfect: usi più comuni (con l impiego di espressioni
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventitrè
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventitrè U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio M Today we do another exercise U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare a
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Ventitrè U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio M Today we do another exercise U Oggi, facciamo un altro esercizio D Noi diciamo una frase in inglese e tu cerca di pensare a
Book 5 Lesson 1 Arabic. I go you (m) go you (f) go to. a mosque a school a shop a garden
 Book 5 Lesson 1 Arabic we we go I go you (m) go you (f) go to a mosque a school a shop a garden Book 5 Lesson 2 Arabic we sit you (f) sit you (m) sit I sit on in a garden a train a house a chair Book 5
Book 5 Lesson 1 Arabic we we go I go you (m) go you (f) go to a mosque a school a shop a garden Book 5 Lesson 2 Arabic we sit you (f) sit you (m) sit I sit on in a garden a train a house a chair Book 5
Before I begin with the notes
 Il Passato Prossimo Before I begin with the notes In this verb : ho mangiato What do you know about this verb? It stems from the verb mangiare, to eat. But how do I know who is doing the eating? That s
Il Passato Prossimo Before I begin with the notes In this verb : ho mangiato What do you know about this verb? It stems from the verb mangiare, to eat. But how do I know who is doing the eating? That s
Lingua inglese Agorà condivisa Istituto professionale indirizzo servizi socio sanitari
 Lingua inglese Agorà condivisa Istituto professionale indirizzo servizi socio sanitari CPIA LECCE Childcare and facilities: day nurseries The description of a Day Nursery da Caring for People, Bellomarì
Lingua inglese Agorà condivisa Istituto professionale indirizzo servizi socio sanitari CPIA LECCE Childcare and facilities: day nurseries The description of a Day Nursery da Caring for People, Bellomarì
Integrazione allo studio di. Inglese B1. a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori
 Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Integrazione allo studio di Inglese B1 a cura della Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Autore dei contenuti: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori Docente del corso: Prof.ssa Laura De Gori i Introduzione all insegnamento di: Inglese
Lesson 16 (A1/A2) Present continuous / Be going to / Future simple
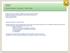 Lesson 16 (A1/A2) Present continuous / Be going to / Future simple In inglese per esprimere il futuro si utilizzano tre diverse costruzioni di base: il present continuous accompagnato da un espressione
Lesson 16 (A1/A2) Present continuous / Be going to / Future simple In inglese per esprimere il futuro si utilizzano tre diverse costruzioni di base: il present continuous accompagnato da un espressione
TEST DI VALUTAZIONE INGLESE
 TEST DI VALUTAZIONE INGLESE 1) What's name? Jane Pitt. a) you b) your c) yours 2) How old are you? a) I have 30 b) 30 years c) I m 30 3) name is Nicholas Ray a) His b) He's c) He 4) is a Fox Terrier. a)
TEST DI VALUTAZIONE INGLESE 1) What's name? Jane Pitt. a) you b) your c) yours 2) How old are you? a) I have 30 b) 30 years c) I m 30 3) name is Nicholas Ray a) His b) He's c) He 4) is a Fox Terrier. a)
ISTITUTO COMPRENSIVO MONTERIGGIONI SCUOLA SECONDARIA DI PRIMO GRADO "A. RONCALLI" CASTELLINA IN CHIANTI ANNO SCOLASTICO 2017/2018 PROGRAMMA SVOLTO
 Libro di testo adottato. High five!, OUP. CLASSE I SEZIONE A MATERIA INGLESE DOCENTE STEFANO PARRINI ANNO SCOLASTICO 2017/2018 PROGRAMMA SVOLTO Presentazione dei moduli affrontati durante l anno scolastico.
Libro di testo adottato. High five!, OUP. CLASSE I SEZIONE A MATERIA INGLESE DOCENTE STEFANO PARRINI ANNO SCOLASTICO 2017/2018 PROGRAMMA SVOLTO Presentazione dei moduli affrontati durante l anno scolastico.
PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE PER COMPETENZE
 PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE PER COMPETENZE ANNO SCOLASTICO 2016-17 CLASSE 1 SEZIONE AT DISCIPLINA Lingua straniera DOCENTE Verrone Clementina QUADRO ORARIO (N. 3 ore settimanali nella classe) Scansione
PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE PER COMPETENZE ANNO SCOLASTICO 2016-17 CLASSE 1 SEZIONE AT DISCIPLINA Lingua straniera DOCENTE Verrone Clementina QUADRO ORARIO (N. 3 ore settimanali nella classe) Scansione
-FUTURO SEMPLICE- (SIMPLE FUTURE)
 Visitaci su: http://englishclass.altervista.org/ -FUTURO SEMPLICE- (SIMPLE FUTURE) In italiano, salvo qualche eccezione, una azione futura viene espressa in un unico modo: utilizzando il futuro semplice
Visitaci su: http://englishclass.altervista.org/ -FUTURO SEMPLICE- (SIMPLE FUTURE) In italiano, salvo qualche eccezione, una azione futura viene espressa in un unico modo: utilizzando il futuro semplice
Passive constructions
 Passive constructions Valenza verbale; Costituenti argomentali e circostanziali; Verbi transitivi e intransitivi Verbi avalenti o monovalenti in italiano e in inglese o a) Verbi meteorologici Ø piove Ø
Passive constructions Valenza verbale; Costituenti argomentali e circostanziali; Verbi transitivi e intransitivi Verbi avalenti o monovalenti in italiano e in inglese o a) Verbi meteorologici Ø piove Ø
PRESENT CONTINUOUS. Si usa per parlare di azioni in corso di svolgimento e si traduce con stare + gerundio. NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE
 PRESENT CONTINUOUS Si usa per parlare di azioni in corso di svolgimento e si traduce con stare + gerundio. AFFIRMATIVE: PRESENT VERB BE (ESSERE) + FORMA BASE + -ING FULL FORMS: SHORT FORMS: I AM PLAYING
PRESENT CONTINUOUS Si usa per parlare di azioni in corso di svolgimento e si traduce con stare + gerundio. AFFIRMATIVE: PRESENT VERB BE (ESSERE) + FORMA BASE + -ING FULL FORMS: SHORT FORMS: I AM PLAYING
U Corso di italiano, Lezione Cinque
 1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Cinque D Ciao, questo è mio figlio. Si chiama Paolo. F Hi, this is my son. His name is Paolo. D Ciao, questo è mio figlio. Si chiama Paolo. M How old is he? D Ha sette anni.
1 U Corso di italiano, Lezione Cinque D Ciao, questo è mio figlio. Si chiama Paolo. F Hi, this is my son. His name is Paolo. D Ciao, questo è mio figlio. Si chiama Paolo. M How old is he? D Ha sette anni.
EURO IN FORMAZIONE ON LINE ANNO III MATERIA: INGLESE LEZIONE 4. Conditional Tense
 Conditional Tense Forma affermativa Soggetto + would ( d) / should + infinito senza to Forma interrogativa Would / should + soggetto + infinito senza to Forma negativa Soggetto + would not (wouldn t) /
Conditional Tense Forma affermativa Soggetto + would ( d) / should + infinito senza to Forma interrogativa Would / should + soggetto + infinito senza to Forma negativa Soggetto + would not (wouldn t) /
Lesson 45: -er, more, less. Lezione 45: -er, more, less
 Lesson 45: -er, more, less Lezione 45: -er, more, less Reading (Lettura) Jason is more active than Kevin in the class. ( Jason è più attivo di Kevin nella classe) This cellphone is cheap, but that one
Lesson 45: -er, more, less Lezione 45: -er, more, less Reading (Lettura) Jason is more active than Kevin in the class. ( Jason è più attivo di Kevin nella classe) This cellphone is cheap, but that one
PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE 2017/2018 LINGUA E CIVILTA INGLESE AB24. CLASSI PRIME TECNICO DOCENTI: Belletti Nunzia, Lopes Francesca
 ISTITUTO DI ISTRUZIONE SUPERIORE ANGELO MOTTI PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE 2017/2018 LINGUA E CIVILTA INGLESE AB24 CLASSI PRIME TECNICO DOCENTI: Belletti Nunzia, Lopes Francesca Legenda: in corsivo si indicano
ISTITUTO DI ISTRUZIONE SUPERIORE ANGELO MOTTI PROGRAMMAZIONE DISCIPLINARE 2017/2018 LINGUA E CIVILTA INGLESE AB24 CLASSI PRIME TECNICO DOCENTI: Belletti Nunzia, Lopes Francesca Legenda: in corsivo si indicano
Pimsleur Italian 11. Listen to this conversation
 Pimsleur Italian 11 DISCLAIMER I recommend only referring to the lesson transcript if you are unsure of a word that is being spoken. Otherwise, we run the risk of disrupting the intended learning process.
Pimsleur Italian 11 DISCLAIMER I recommend only referring to the lesson transcript if you are unsure of a word that is being spoken. Otherwise, we run the risk of disrupting the intended learning process.
Lower intermediate - Lesson 1
 Lower intermediate - Lesson 1 Gli Ausiliari Be, Have e Do In inglese si distinguono tre diversi tipi di verbi: gli ausiliari, i modali e tutti gli altri verbi. In questa lezione studieremo i verbi ausiliari
Lower intermediate - Lesson 1 Gli Ausiliari Be, Have e Do In inglese si distinguono tre diversi tipi di verbi: gli ausiliari, i modali e tutti gli altri verbi. In questa lezione studieremo i verbi ausiliari
